With building information modeling, architects and engineers can more effectively optimize building systems to reduce waste and maintenance. It also lets professionals working on new construction or renovations more efficiently design effective solutions. But how does building information modeling work, and why is it used?
What is building information modeling (BIM)?
BIM – Building Information Model – is what digital blueprints are made of. It’s a source of building data that is often available for new or in-development buildings.
Both the International Standards Organizations and the US National Building Information Model Standard Project Committee define BIM in a very similar way. Both organizations roughly define it as a digital representation of the functional and physical characteristics of built assets.
As a digital representation, BIM expands the capabilities of architects and engineers to design with three-dimensional models. It also allows them to portray the functionality of different building systems accurately.
Is there any difference between building information modeling and building information management?
Building information modeling and building information management are two distinct processes even though they are both commonly abbreviated as BIM. The management of building information deals with the data management necessary for accurate modeling. Building information management ensures all data remains up-to-date and properly formatted. These two terms are also different from building management systems.
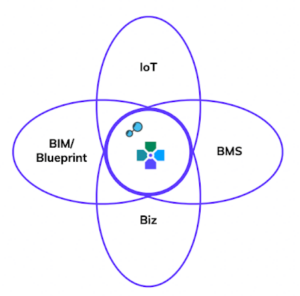
Proptech and BIM work together in conjunction
A BIM model represents a large investment in both time and resources. Therefore, utilizing BIM data via proptech applications to extract as much value as possible is a sound strategy.
To break it down into sections and explain the symbiosis between the different areas can look like this:
Five areas working together for better impact
They are not stacked, but rather all sections feed off each other in order to optimize and create a better value proposition.
- BIM
The blueprint and source for building data.
- IoT
Internet of Things is the network that facilitates communication between devices and the cloud, as well as between the devices themselves.
- BMS
A control system to monitor and manage the mechanical, electrical and electromechanical services in a facility. Such services can include HVAC (Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning).
How does building information modeling work?
Although BIM uses a CAD model as its basis, BIM pairs building information with building systems in a CAD model. By tying building information to building systems, BIM turns a static CAD model into a dynamic model. It can showcase which walls are load-bearing and areas where electrical wiring can be routed. This allows architects, engineers, and stakeholders to collaborate more efficiently.
Mature BIM uses a single model that all stakeholders can work on. With a single model, all trades can work collaboratively with equal information. This lets teams streamline the design process as all stakeholders are always aware of limitations imposed by the other trades.
Overall, BIM works in a similar way to digital twin technology, except it focuses more specifically on buildings during the design and construction phase. Although BIM can help with building operations, the future of digital twin technology offers more opportunities for optimizing building operations.
What technology is used in BIM?
BIM requires CAD models, data management systems, and BIM software. Essentially, the models layer different CAD drawings and then tie them together with building data to showcase the interworkings of a building’s design.
What is a BIM object?
Each distinct product of a building is considered a BIM object. BIM software defines each object’s characteristics, properties, parameters, and interactions. This allows stakeholders to understand the interworkings of building systems better.
Different levels of BIM
Refer to the maturity level of the modeling used. Currently, there’s a total of four different BIM levels starting from level 0 and going to level 3.
- Level 0: Uses paper-based CAD drafting with two dimensions. No use of BIM.
- Level 1: Expands use to three-dimensional CAD modeling for conceptual drafting then turned into two-dimensional drawings for approval.
- Level 2: Builds upon level 1 BIM by promoting collaboration amongst stakeholders. All stakeholders have a 3D CAD model to streamline the exchange of information for more accurate building data.
- Level 3: Instead of each stakeholder having a 3D CAD model, all stakeholders can collaborate on a single shared model. This eliminates the risk of conflicting information and ensures all stakeholders can supply accurate building information that other stakeholders can build from.
What is BIM software used for?
BIM software provides the tools necessary to create building information models based on CAD models and defined objects. They provide a collaborative workspace for architects, engineers, facility managers, and construction teams to design and construct new buildings or renovations. With a single source of information, BIM software minimizes the risks of miscommunication.
Benefits of building information modeling
Building information modeling offers a wide range of benefits by improving the experience of every stakeholder. From the architects and engineers designing the building to the construction teams making the building, BIM offers more detailed information and easier collaboration.
On the design side, BIM makes cost estimates more accurate and easier to create. With each object identified in the design, the entire cost estimation process can be automated. It also makes it easier for architects and engineers to communicate the design vision of the end building to the stakeholders hiring the architects and engineers.
On the construction side, BIM makes it easier for construction teams to collaborate with the architects and engineers during the construction phase. All trades can collaborate on a single cloud-based BIM model. They can also bring the model into the field for more accurate requests for information.
Differences between BIM and CAD
CAD offers the base model of a building and a model for each engineering discipline. However, CAD cannot provide the interactions between the architect’s building design and each engineering discipline’s design. This can lead to unforeseen issues during the construction phase resulting in expensive change orders. BIM connects this information into a single model to prevent these issues from forming.
Is BIM sustainable?
With BIM, designers can more accurately portray the overall sustainability of a planned building. An entire building’s design and inner workings can be shown in a single BIM model allowing teams to collaborate on ways to improve a building’s sustainability more effectively. Whether it’s altering the location of a wall to run a hot water loop closer to the kitchen or rerouting water lines to make room for more efficient electrical wiring, BIM promotes the collaboration necessary for sustainable design.
By offering this level of collaboration, teams can more effectively reach sustainability goals set by LEED, BREEAM, or ESG Green Buildings.
Why is building information modeling important?
As buildings become increasingly complex, building information modeling becomes a necessity to accurately portray building systems. Engineering disciplines must work closely together alongside the architects and other stakeholders to successfully design modern buildings. The systems of a modern building all work alongside each other, so a tool to bring this information into a single model is necessary.
The future of BIM
In the future, BIM software will continue expanding in capabilities to incorporate more accurate building information. It might also see use in building performance analysis to help improve the overall function of a building designed with BIM.
ProptechOS offers unique solutions that leverage the capabilities of BIM to help stakeholders optimize real estate investments through sustainable building initiatives.

Dr. Erik Wallin
Chief Ecosystem Officer, and founder of ProptechOS and RealEstateCore is recognized as a leader in Building Operating Systems (BOS) and making the buildings of the world smarter. He holds an MSc and a Ph.D. in Media and Computer Science from KTH Royal Institute of Technology.
Read his full bio and information here.